Iridium Foil/Sheet
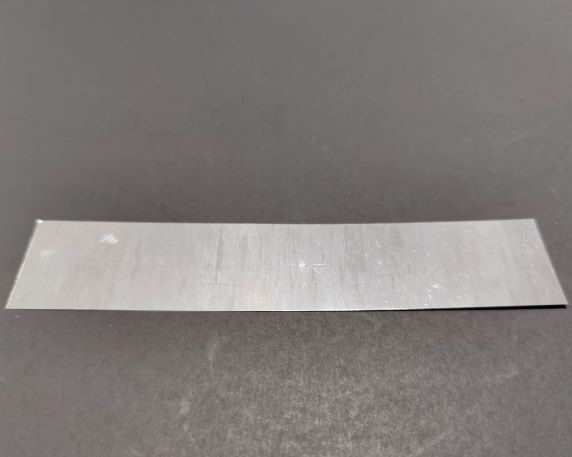

| Product | Iridium Foil/Sheet (Ir Foil/Sheet) |
| Part Number | IR-01 |
| CAS Number | 7439-88-5 |
About Iridium (Ir) Foil
Iridium, a metal element, has the element symbol Ir, atomic number 77, atomic weight 192.22, and the element name comes from Latin, with the original meaning of “rainbow”. The content of iridium in the earth’s crust is one part per ten million, and it is often dispersed in various ores in alluvial deposits and placer deposits together with platinum series elements.
Iridium is a platinum group metal and is white like platinum with a little yellow. Iridium is hard and fragile, and its melting point is very high, so it is difficult to cast and plasticize. Therefore, the manufacturing process generally uses powder metallurgy. Iridium is the only metal that maintains excellent mechanical properties in air above 1600 °C. Its boiling point is extremely high, ranking 10th among all elements. Iridium exhibits superconductor properties below 0.14 K.
The elastic modulus of iridium is lower than that of osmium, which is the second highest among all metals. Its shear modulus is very high and Poisson’s ratio is very low, so it has high rigidity, making the processing and production process of iridium very difficult. Although it is not easy to produce and expensive, iridium has many applications, including strengthening mechanical strength under extreme conditions. Iridium is one of the most corrosion-resistant metals.
Many high melting point oxide single crystals are grown in crucibles made of pure iridium. Pure iridium, platinum iridium alloys and iridium rhodium alloys are mostly used to make scientific instruments, thermocouples, resistance wires, etc. Adding iridium to platinum can improve the corrosion resistance of platinum in water, acid and halogen and the mechanical strength below 500°C. However, with the increase of iridium content, the oxidation weight loss of the alloy in air above 900°C also increases. The platinum iridium alloy containing 10% iridium and 90% platinum is used to make the international standard meter ruler because of its extremely small coefficient of expansion. The kilogram prototype in the world was also made of platinum iridium alloy.
NCE provides various Iridium Foil, Iridium Sheet, Iridium Target, Iridium Wire, Iridium Filament, Iridium Crucible, Pt-Ir alloy products etc. Ultra-thin Iridium foils, as thin as 0.001” (0.025 mm) and ultra-fine Iridium wires are available. Please contact us for more details. Get a Quote Now! For other metals and precious metals, please check our Metals/Precious Metals catalog page.
Application of Iridium:
The high melting point and high stability of iridium make it important for many special occasions, but the brittleness and high temperature loss of iridium limit its application to a certain extent.
The earliest application of iridium was as a pen tip material, and later applications for injection needles, balance blades, compass holders, and electrical contacts were proposed.
The iridium crucible can be used to grow refractory oxide crystals. The crucible can work at 2100~2200℃ for several thousand hours and is an important precious metal vessel material.
The high temperature oxidation resistance and thermoelectric properties of iridium make the iridium/iridium rhodium thermocouple the only precious metal temperature measurement material that can measure high temperatures up to 2100℃ in the atmosphere. It can also be used as a container material for radioactive heat sources. In addition, anodized iridium film is a promising electrochromic material. Ir-192 is a gamma-ray source, which can be used for non-destructive testing and radiochemotherapy.
At the same time, iridium is a very important alloying element, and some iridium alloys are used in some key sectors. Iridium compounds also have their own special uses.
Properties of Iridium:
The melting point is 2450℃, and the service temperature of iridium products can reach 2100~2200°C.
The elastic modulus is high (538.3 GPa), the Poisson coefficient is low (0.26), and the low temperature plasticity is very poor.
It is the most corrosion resistant. The dense state of iridium is insoluble in all inorganic acids and is not corroded by other metal melts, such as molten lead, zinc, nickel, iron, gold, etc. It can withstand the erosion of many molten reagents and high-temperature silicates.
Like other platinum group metal alloys, iridium alloys can firmly adsorb organics and can be used as catalyst materials.
IrO₂ is formed in air or oxygen above 600℃ and decomposed at 1100℃. The volatilization amount of iridium in the air at 1227°C is 100 times that of platinum. Iridium can be smelted in high frequency or intermediate frequency furnaces, electric arc furnaces, electron beams, etc. Iridium has good plasticity above 1600°C and is usually hot processed.
Typical Dimensions of Iridium Foil/Sheet
| Type | Thickness | Width & Length |
| Iridium Foil | 0.001” (0.025 mm) | 1”x5”, 1”x1”, 2”x2” |
| Iridium Foil | 0.002” (0.05 mm) | 1’’x5’’, 1’’’x1’’, 2’’x2’’ |
| Iridium Foil | 0.003” (0.075 mm) | 1”x5”, 1”x1”, 2”x2” |
| Iridium Foil | 0.004” (0.1 mm) | 1”x5”, 1”x1”, 2”x2” |
| Iridium Purity: 99.8%, 99.9% | ||
| .001” and .002” are the typical thicknesses. Custom work is available on request with the minimum order quantity. | ||
We can also offer thicker Iridium Sheets. Please contact us with your requirements.
Order Information
Inquiries and orders should include the following information:
- Dimensions/Tolerance
- Quantity
Packing and Storage
Standard Packing: carton box
Physical Properties of Iridium (Ir)
| Phase | Solid |
| Melting point | 2450°C |
| Boiling point | 4130°C |
| Density | 22.65 g/cm3 |
| Solubility | Insolubility in water |